Testosterone is a hormone that occurs naturally in both men and women. In men testosterone is produced in the testes, and in women testosterone is produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands.
Testosterone is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics in men, but it also plays vital roles in the maintenance of lean muscle mass, bone health, brain health, metabolic function, sexual function, mental acuity, energy, and mood enhancement for both men and women.
Comparatively, men need more testosterone than women to feel good and be healthy. However, the small amount needed by women is just as important for vitality and good health.
What is testosterone replacement therapy?
Testosterone replacement therapy is exactly what the name implies. Testosterone replacement puts back into the body what the body is no longer able to produce on its own. The goal during testosterone replacement is to restore testosterone to physiologically optimal levels.
Who should consider testosterone replacement therapy?
Candidates for testosterone replacement vary based on age, health history, hormone levels, and symptoms. Men over the age of 22 and women past their years of fertility may be candidates for testosterone replacement depending upon their baseline testosterone levels and how they feel.
The treatment process involves evaluating health history and symptoms, routine blood work, and meeting with a physician who is experienced in prescribing testosterone replacement. When treatment is done correctly, it will be tailored to each person’s unique physiological needs.
When and why should someone consider testosterone replacement?
Hormone levels decline over time with age. Age-related hormone decline is a reality that no one escapes. Commonly men and women will experience a decline in testosterone production during their 30s and beyond. However, for some people this decline will occur during their 20s. The reasons for early hormone decline vary, but can include head injuries, hormones in the food supply, chronic or severe stress, toxins in the environment, certain medications, some health conditions, and genetics.
Men over 22 and women past their years of fertility should be evaluated if they are experiencing any of the following symptoms: fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction (for men), difficulty achieving orgasm (for men and women), low motivation, poor exercise performance and slow recovery from exercise, difficulty building lean muscle mass, mood issues, and poor mental acuity.
In addition to symptom relief, keeping testosterone levels optimized helps to promote vitality, longevity, and good overall health (including heart health, bone health, brain health, and metabolic health).
Where and how to administer testosterone
The best methods for getting testosterone into a person’s body safely and effectively are by self-administered injection or by topically applied cream.
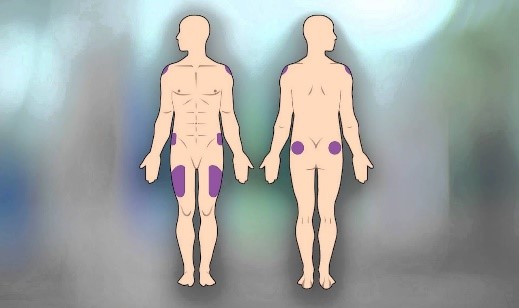
When done by injection, testosterone is typically injected intramuscularly into the quadriceps muscle, the gluteal muscle, or the deltoids. Injecting two times per week works well for most people, but different injection schedules work for different people. It’s also worth noting that some people prefer subcutaneous injections over intramuscular injections. Your doctor will help to determine what’s optimal for you in terms of safety, effectiveness, and personal preference.
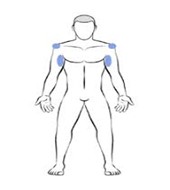
Application sites for men using topically applied testosterone cream are generally the neck, shoulders, or scrotum. Application sites for women are typically the waist, abdomen, thighs, buttocks, backs of the, knees, calves, or genitals.